I. What is Index?
A data structure is used to locate and fast access data in tables or views
- Help reducing the amount of access to memory during query execution
-> Increase database query performance.
- Two types of indexes:
- Clustered
- Non-clustered
II. What is the index database used for?
Example:
select * from table_name
where column_name = val
-
If there is no index for the
column_namecolumn, the system will scan all the rows of thetable_nametable to search for the row that satisfies conditioncolumn_name = val -
An index points to the address of data in a table (like table of contents in a book)
-
Indexes can be created for one or more columns in a table.
- Create by default for primary keys, foreign keys
- It is possible to create additional indexes for columns if needed
III. The structure of the index
- Search Key: contains a copy of the indexed column’s values
- Data Reference: contains the pointer to the address of the record with the corresponding index column value
IV. Types of indexes
B-tree
- The default index type
graph TD 20,40 --> 10; 10 --> 5; 10-->15 20,40 --> 30,33; 30,33 --> 25,28; 30,33 --> 31; 30,33 --> 35 20,40 --> 50,60; 50,60 --> 45; 50,60 --> 55; 50,60 --> 65
Features:
-
Index data is organized and stored in the form of tree (root, branch, leaf)
-
The values of nodes increase from left to right
-
The B-tree index is used in comparision expressions:
=,>,>=,<,<=,BETWEEN,LIKE-> Good forORDER BYstatement -
When searching for the node, it starts from the root node, and then comes to the branch and leaf, until all satisfied data are found.
Syntax
--- create index
CREATE INDEX id_index ON table_name
(column_name [, column_name…]) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX id_index
(column_name [, column_name…])
--- delete index
DROP INDEX index_name ON table_name
For more details, visit here
Hash
- Based on Hash function algorithm.
- Corresponding to each block of data, index will generate a bucket key (also called hash value) to distinguish.
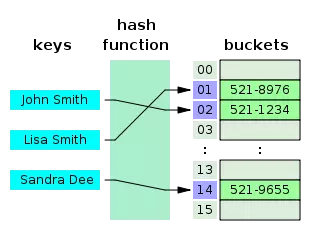
Features:
- Hash index should be used only in
=and<>(not equal to operator). (Don’t use for operators to find a range of values, like>or<) - The
ORDER BYis not optimized when using Hash index. (can’t find the next element in the order) - Hash is faster than B-tree
Syntax
--- create index
CREATE INDEX id_index
ON table_name(column_name [, column_name…]) USING HASH;
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD INDEX id_index(column_name [, column_name…]) USING HASH;
For more details about Hash index, visit here
Storage Engine
- When choosing the index type, it also depends on whether or not the Storage Engine supports the type of index.
| Storage Engine | Supported Index Types |
|---|---|
| InnoDB | Btree |
| MyISAM | Btree |
| MEMORY/HEAP | Hash, Btree |
| NDB | Hash, Btree |
V. How to use index database effectively?
-
SHOULD INDEX:
- The columns used in
WHERE,JOIN,ORDER BY
- The columns used in
-
SHOULDN’T INDEX:
- Small tables, containing little data
- Tables are updated and inserted data regularly
- Columns contain so many NULL values
- Columns are regularly updated
⚠️ Downside of indexing is that it takes up more memory to store.
