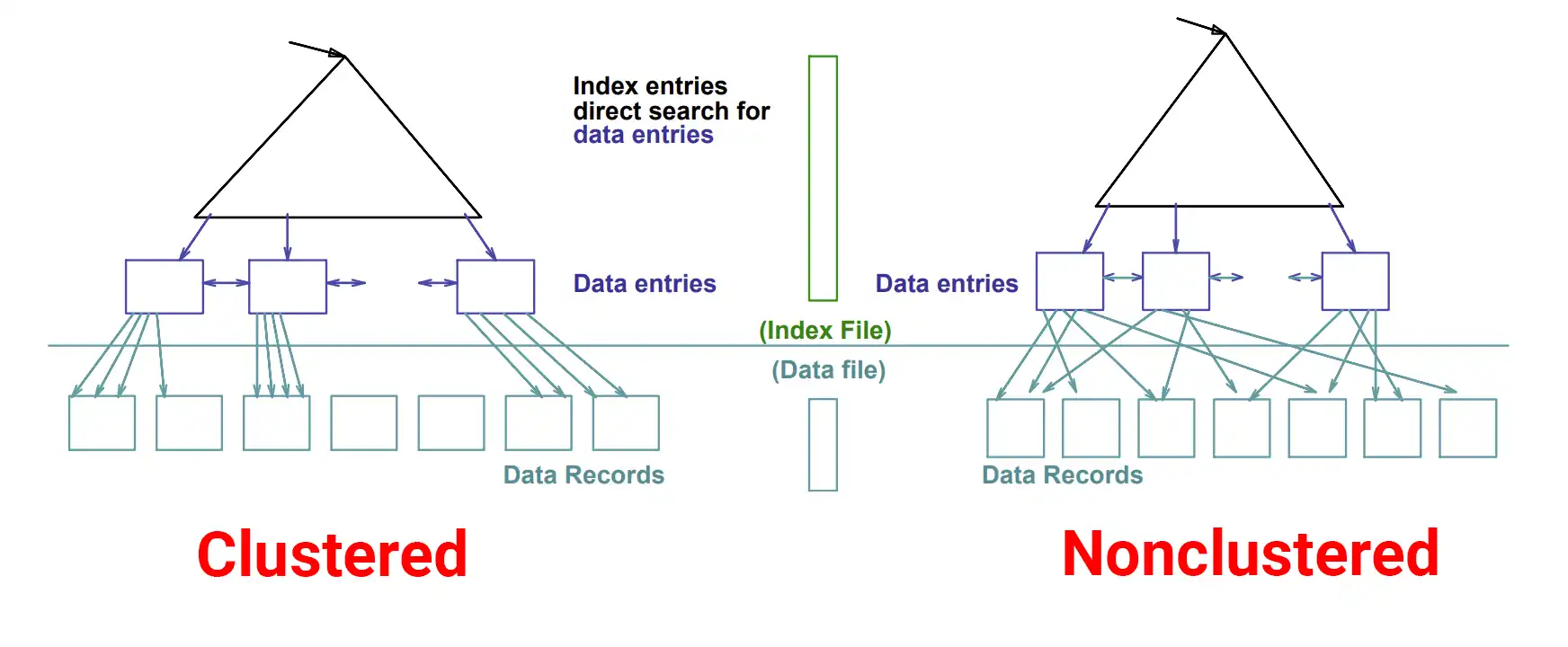
Clustered index
-
Store the records in an ordered structure based on its key value
-
Each table just have one clustered index (because the data can only be arranged in one order), and a table with clustered index is called clustered table
-
Data in clustered index are organized like B-tree
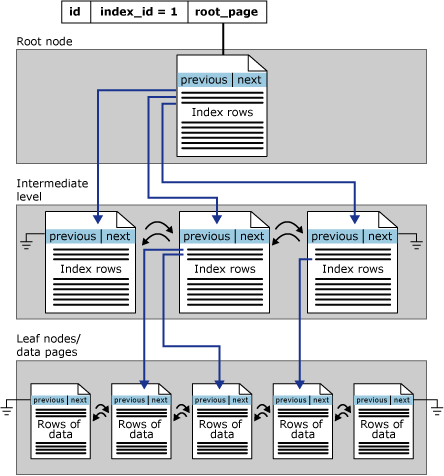
- The root node and the intermediate node contain index pages for storing the indexes of the records
- The leaf node contains the data pages of the table
- Pages within each level of the index are linked in a double linked list structure
In SQL Server
-
When creating the table with the Primary Key (PK), SQL Server automatically creates a clustered index on the PK columns.
-
When user add the PK to a table which has a clustered index, SQL Server will force the PK to use non-clustered index
Syntax
--- create clustered index (table doesn't have PK)
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX index_name
ON schema_name.table_name (column_list);
--- query
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
Non-clustered index
-
Different from clusterd index: sorts and stores data separately from records in the table
-
Data is copied from selected columns from a linked table.
-
Organize data in Btree structure
-
A table can have one or more non-clustered indexes. Each non-clustered index can consist of one or more table columns.
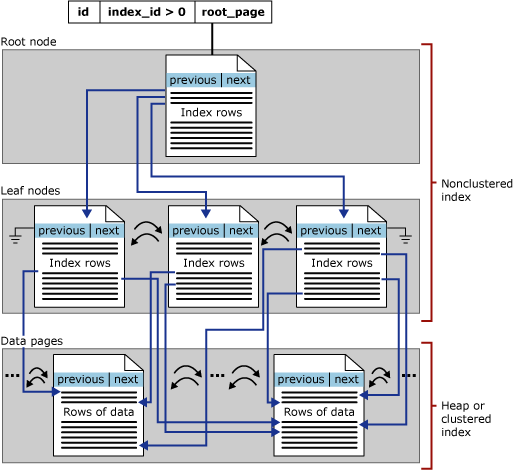
- Apart from storing the index key values, the leaf nodes also store pointers to the records containing the key values (also called row locators)
Syntax
--- create non-clustered index
CREATE [NON-CLUSTERED] INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column_list);
Other stuffs
Rename index in SQL Server
- Use
sp_renameStored Procedure
EXEC sp_rename index_name, new_index_name, N'INDEX';
--- or
EXEC sp_rename @objname = N'index_name', @newname =
N'new_index_name', @objtype = N'INDEX';
Unique index
-
Can be one or more columns.
-
Can be clustered or non-clustered
--- create unique index
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column_list);
Disable indexing in SQL Server
-
Disabling the index speed up updating process on a table
ALTER INDEX index_name ON table_name DISABLE; -
Disable all indexes
ALTER INDEX ALL ON table_name DISABLE; -
If an index is disabled, the optimizer will not use that index to plan the query execution
-
SQL Server retains index definition in metadata and index statistics in non-clustered indexes.
-
But when users disable index on view, SQL Server will delete all index data
-
If a clustered index of a table is disabled, the data of the table cann’t be accessed using
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATEandDELETEuntil the clustered index is rebuilt/delete.
Enable indexes in SQL Server
- It needs to be rebuilt to reflect new data in the table.
--- alter index/create index
ALTER INDEX index_name
ON table_name
REBUILD;
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column_list)
WITH(DROP_EXISTING=ON) -- it drop the index first, then rebuilt it
ALTER INDEX ALL ON table_name
REBUILD;
-- DBCC DBREINEX
DBCC DBREINDEX (table_name, index_name);
Delete indexes in SQL Server
DROP INDEX [IF EXISTS] index_name
ON table_name
-- for dropping multiple indexes from one/multiple tables
DROP INDEX [IF EXISTS]
index_name1 ON table_name 1,
index_name2 ON table_name 2,
...;
⚠️ It can’t delete indexes create by PK or UNIQUE CONSTRAINT (use ALTER TABLE DROP CONSTRAINT instead)
Filtered index in SQL Server
- is a non-clustered index with an expression that specifies which records should be added to the index
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column_list)
WHERE predicate
Example
SELECT
SUM(CASE
WHEN phone IS NULL
THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS [Has Phone],
SUM(CASE
WHEN phone IS NULL
THEN 0
ELSE 1
END) AS [No Phone]
FROM sales.customers;
CREATE INDEX ix_cust_phone
ON sales.customers(phone)
INCLUDE (first_name, last_name)
WHERE phone IS NOT NULL;